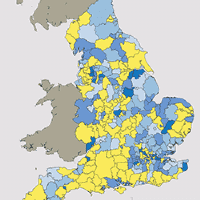
■ It’s been five years since the publication of the NPPF, and plan making remains slow. Only 41% of local authorities in England have adopted an up-to-date plan, up from 25% two years ago. Many adopted plans are failing to set targets that meet housing need. Adopted planning targets in England are 88% of objectively assessed need for housing. See Plan-making in numbers.
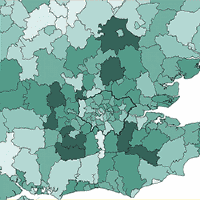
■ Assessing need based on market strength would start to address housing affordability, but could lead to big increases in housing-need numbers in and around London. Some districts will have to find additional housing land from as soon as 2018 if these figures are used in the Housing Delivery Test identified in the Housing White Paper. See London under pressure.
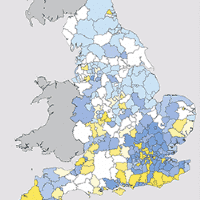
■ Our positive planning index has identified the top 10 local authorities which need to identify more land for housing, based on local plan status, five year land supply, Housing Delivery Test and housing affordability. These authorities have strong links to London, but their ability to build homes is often constrained by the Green Belt. See Impact of housing delivery test.
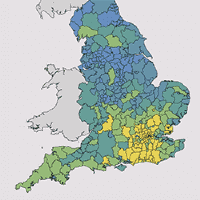
■ 61 local authorities have lost at appeal due to not having a five-year land supply in the year to April 2017. A further 61 authorities have a published housing land supply of less than five years. Across England, local authorities have on average 5.3 years’ land supply, down from 5.4 years last year. See Plan-making in numbers.